
- #WHAT IS READYBOOST CACHE DRIVER#
- #WHAT IS READYBOOST CACHE PORTABLE#
- #WHAT IS READYBOOST CACHE WINDOWS 7#
- #WHAT IS READYBOOST CACHE WINDOWS#
The core idea of ReadyBoost is that a flash memory (e.g. As the price of RAM decreased and more RAM was installed in computers, the mitigations provided by ReadyBoost to systems with insufficient memory decreased.
#WHAT IS READYBOOST CACHE WINDOWS#
System performance with ReadyBoost can be monitored by Windows Performance Monitor. However, increasing the physical memory (RAM) from 512 MB to 1 GB (without ReadyBoost) reduced it to 0.8 seconds. In one test case, adding 1 GB of ReadyBoost memory sped up an operation from 11.7 seconds to 2 seconds. Performance Ī system with 512 MB of RAM (the minimum requirement for Windows Vista) can see significant gains from ReadyBoost. ReadyBoost is not available on Windows Server 2008.
#WHAT IS READYBOOST CACHE PORTABLE#
ReadyBoost is not compatible with portable media devices such as mobile phones or cameras, or other devices with emulated storage.
#WHAT IS READYBOOST CACHE DRIVER#
#WHAT IS READYBOOST CACHE WINDOWS 7#
Windows 7 supports multiple flash drives for ReadyBoost, so performance improvement similar to RAID 0 can be expected. The initial release of ReadyBoost for Windows Vista supported one device.The performance differences between these file systems are negligible with ReadyBoost. As the ReadyBoost cache is stored as a file, the flash drive must be formatted as FAT32, NTFS, or exFAT in order to have a cache size greater than FAT16's 2 GB filesize limit if the desired cache size is 4 GB (the FAT32 filesize limit) or larger, the drive must be formatted as NTFS or exFAT. Windows 7 also supports the newer exFAT file system. Vista's ReadyBoost supports NTFS, FAT16, and FAT32 from SP1 onwards.The Microsoft Windows Client Performance group recommends a flash-memory-to-system-RAM ratio of between 1:1 and 2.5:1.The device must be capable of 2.5 Mbit/s read speeds for 4 kB random reads spread uniformly across the entire device, and 1.75 Mbit/s write speeds for 512 kB random writes spread uniformly across the device.The device must have an access time of 1 ms or less.


In Windows 7 or later with NTFS or exFAT formatting, the maximum cache size is 32 GB per device. In Vista or with FAT32 formatting of the drive, the maximum is 4 GB. When a compatible device is plugged in, the Windows AutoPlay dialog offers an additional option to use the flash drive to speed up the system an additional ReadyBoost tab is added to the drive's properties dialog where the amount of space to be used can be configured. Flash devices typically are slower than a mechanical hard disk for sequential I/O, so, to maximize performance, ReadyBoost includes logic that recognizes large, sequential read requests and has the hard disk service these requests. This caching applies to all disk content, not just the page file or system DLLs.
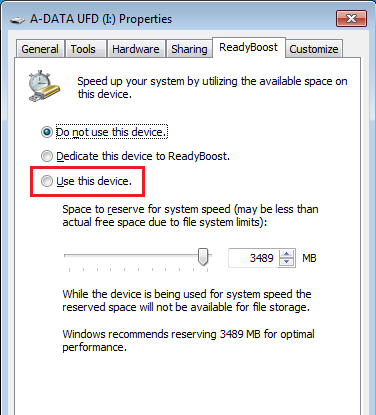
Using ReadyBoost-capable flash memory ( NAND memory devices) for caching allows Windows Vista and later to service random disk reads with better performance than without the cache.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
